The Painful Knees: What Are The Causes, Risk Factors, Management And When To See The Doctor?
Introduction:
Knees are complex, weight-bearing joints that provide our body with flexibility, support, and a wide range of motion. However, it is also one of the most extremely vulnerable joint of the body and can be injured from trauma, arthritis, or everyday stress or strain. Hence knee pain is a common ailment in our daily lives, which can lead to problems ranging from minor discomfort to some serious disability. Fortunately, there are many forms of knee pain treatment and known remedies for knee pain today.
Apart from aging, which is the biggest risk factor for knee pain, there are a number of other conditions when an individual is more susceptible to knee pain. Some of these include:
- Obesity: the excess weight increases stress and pressure on the knee joints wearing it away.
- Overuse: can lead to muscle fatigue and excessive usage massively stresses the joint.
- Instability: tight or weak muscles offer less joint support and stability and the knee is more susceptible to wear and tear and injuries without an effective support system.
- Mechanical problems: structural or congenital abnormalities, such as having one leg shorter than the other or flat feet can increase risk of knee pain.
- Athletic or sports activities: over usage in athletic or sports activities can cause wear or tear or injuries which can cause pain and make the knee joint more vulnerable.
- Past injuries: past injuries make the knee joint more vulnerable and susceptible to problems.
Anatomy of The Knee Joint
The knee is the largest weight-bearing joint in our body. It is made up of four main things: bones, ligaments, cartilage and tendons.
- Bones: The three bones which make the knee joint are:
- thighbone, which is also known as the femur
- shinbone, which is also known as the tibia
- kneecap, which is also known as the patella.
- Ligaments: There are four main ligaments in our knee joint which act like strong ropes to hold the bones together and keep the knee in place. These include:
- The Medial Collateral and the Lateral Collateral ligaments: which are found on the sides of the knee and control the sideways movements of the leg.
- The Anterior and the Posterior Cruciate ligaments: which are found on the inside of the knee and move the leg backwards and forwards.
- Cartilage: There are two types of cartilages in the knee:
- Articular cartilage: This is a slippery material which covers the ends of the thigh bone and shinbone, and the back of the kneecap, which helps the knee bones glide smoothly across each other as we bend or straighten out our
- Meniscal cartilage or meniscus: these are two wedge-shaped pieces that act as shock absorbers between the shinbone and thighbone, called the Medial and the Lateral The menisci help to cushion and stabilize the knee joint, which is why they are tough and rubbery.
How Is Knee Pain Managed?
Knee pain treatment is exhaustive and there are many remedies for knee pain such as by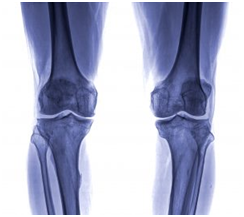 medications, physical therapy, or other strengthening exercises and surgery. Diagnosing the exact reason for knee pain can be challenging because of the wide range of possible causes. A comprehensive medical history and a thorough physical examination are vital. X-rays are mostly taken to detect bone injuries and degenerative arthritis, but computed tomography scans (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans are often used to identify soft tissue injuries. Sometimes Radionuclide bone scans and Arthroscopy may also be needed to aid diagnosis.
medications, physical therapy, or other strengthening exercises and surgery. Diagnosing the exact reason for knee pain can be challenging because of the wide range of possible causes. A comprehensive medical history and a thorough physical examination are vital. X-rays are mostly taken to detect bone injuries and degenerative arthritis, but computed tomography scans (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans are often used to identify soft tissue injuries. Sometimes Radionuclide bone scans and Arthroscopy may also be needed to aid diagnosis.
Knee pain treatment depends upon what exactly is the cause and constitutes of:
1) Medications: These include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and other over-the-counter medications like Aspirin, Acetaminophen (Tylenol), Ibuprofen (Neurofen) or Naproxen. Rub-off painkillers are also commonly used.
2) Activity limitations and rest: To speed up recovery and protect against further damage, activities such as kneeling, squatting or playing sports should be avoided. There should be ample rest to the knees to reduce the repetitive strain. Minor injuries may require only a few days of rest but severe damage is likely to need a longer recovery time.
3) Ice, heat, compression and elevation: reduces the pain, swelling and inflammation.
4) Physiotherapy: includes stretching and muscle strengthening exercises to stabilize the knee joint. Exercises that improve flexibility, balance and movements are also important.
5) Supports & braces – Knee braces or sleeves can also be used to support the joint and restrict range of movement. Compression, which is a wrap around the knee prevents swelling and edema (fluid buildup within the joint)
6) Surgery: Is usually used as the last resort. These include Arthroscopic surgery, Partial and total knee replacement surgery of the knee.
When To See A Doctor?
At what point do you need to see a doctor for knee pain treatment?
When there is:
- Difficulty bearing weight on the knees
- Swelling of the knee
- Obvious deformity in the leg or knee
- Severe or persisting pain
- Inability to bend or straighten the leg
What To Expect When I Visit The Pain Relief Clinic
A typical visit will involve our doctor first understanding your medical history, concerns and previous experience with other pain treatments.
For patients who have consulted many people but have yet to receive a clear diagnosis, selecting an affordable imaging scan might be recommended to confirm the cause of your pain..
Some patients have already done scans with other doctors for their pain condition but are still not clearly told what they suffer from.
Dr Terence Tan is happy to offer you a second opinion and recommend how best to manage your condition.
We also see patients who already have a confirmed diagnosis from specialist pain doctors, but are "stuck” because treatment options offered are not practical or acceptable.
We can help by discussing options that you might have potentially never been told of.
A common experience is when a patient has already consulted a specialist doctor for pain management and is told to consider orthopaedic surgery which they find too aggressive.
Or they may have seen doctors for their pain and were prescribed painkillers with potential side effects which made them feel uncomfortable.
Many of our patients have also first tried complementary treatments or acupuncture with traditional Chinese pain doctors.
They look for a second opinion after finding any relief experienced from other treatments to be temporary or requiring repetitive treatments, which add up to time and cost.
Especially in such situations, we emphasize using non-invasive medical technology you likely have not been told about .
This can make a big difference to your results.